The Environmental Health and Safety office at UC Santa Cruz has a useful online decay calculator. Given an initial amount of material and an interval of time, it will calculate the amount of material remaining for six specific isotopes.
The calculator works with an exponential function of the form
A(t) = A0 e –l t
Each isotope has a known lambda value l , which determines its half-life. (How?) This is the same lambda value used in Rutherford and Soddy's law of radioactive change.
 Amounts of material are measured in Curies. One Curie is the amount of a given nuclide that undegoes 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second (dps). The Curie is named for Marie and Pierre Curie, who together conducted early research into radioactivity.
Amounts of material are measured in Curies. One Curie is the amount of a given nuclide that undegoes 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second (dps). The Curie is named for Marie and Pierre Curie, who together conducted early research into radioactivity.
Use the decay calculator to calculate the decay of 500 milliCuries (mCi) of phosphorus-32 from your choice of reference date to today. Calculate the half-life. How long does it take for 500 mCi of 32P to decay below 1 microCurie (mCi)? How does this decay time compare with the storage guideline of 10 half-lives?.
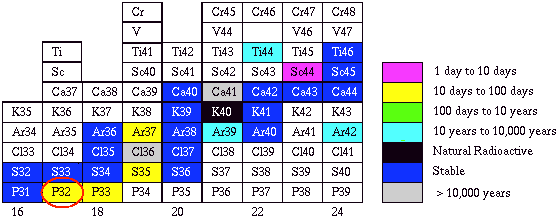
To find the half-lives of isotopes not supported by the decay calculator (and much more information), explore the Table
of the Nuclides page at Brookhaven National Lab.
 Amounts of material are measured in Curies. One Curie is the amount of a given nuclide that undegoes 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second (dps). The Curie is named for Marie and Pierre Curie, who together conducted early research into radioactivity.
Amounts of material are measured in Curies. One Curie is the amount of a given nuclide that undegoes 3.7 x 1010 disintegrations per second (dps). The Curie is named for Marie and Pierre Curie, who together conducted early research into radioactivity.
