| Example: Airline Crash Investigations | Click here to open an associated Mathcad worksheet: |
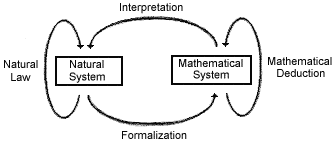
Whenever a plane crashes, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is responsible for carrying out an investigation to determine its cause. This usually involves building a mathematical model, on a computer, of the airplane and the conditions under which it crashed. In terms of the modeling process outlined above:

|
Natural law represents the actual conditions and causes for the crash. These might be complex combinations of many different factors, such as weather, mechanical failure, or pilot error. |
|
Formalization represents the choices which the computer programmers must make concerning the essential features of the aircraft and the external conditions. What mathematical objects (equations, graphs, etc.) simply and accurately describe different possible weather conditions? How should complex engine behaviors and unpredictable pilot actions be represented? Ideally, each important factor must be accounted for in the model, and so must all of their essential interactions. |

|
Mathematical deduction is the investigation of possible crash scenarios within the model. Once all of the various cause and effect relationships, and their various interactions, have been expressed in mathematical terms in a computer program, the program can be run – that is, the mathematical computations can be carried out by the machine – under a variety of different initial conditions. Countless model airplanes may be "crashed" in a search for a match with the known facts. |

|
Interpretation is the part of the process that the FAA might report at a news conference. For example, if no scenario involving various pilot errors or unusual weather conditions results in a model crash at all like the actual one, then the FAA may claim that these possibilities have been ruled out, and direct their efforts to an investigation of engine failure. If, on the other hand, a model simulation of the aircraft's encounter with a windy downburst produces a close match of what was observed, then the case may be closed. |
|
|
|
|
| Back to Contents | ||